A persistent autoimmune condition called rheumatoid arthritis (RA) produces inflammation in the joints, which results in discomfort, stiffness, and swelling. Millions of individuals throughout the world suffer from RA, which is a prevalent ailment.
Depending on the population being researched and the diagnostic criteria being employed, RA prevalence varies. The prevalence of RA among adults in the United States is thought to be 1.3%. This indicates that approximately 1 in 100 adults in the US have RA. Incidence of RA rises with age, and it is more prevalent in women than in males. Although it is less common in these age ranges, RA can also strike children and teenagers.
A person’s quality of life may be significantly impacted by RA, which can also cause considerable disability. A person’s overall prognosis can be improved and the risk of joint damage and disability can be reduced with early identification and treatment of RA. It is crucial to contact with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan if you have any health concerns or are exhibiting symptoms that could indicate RA.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is thought to be caused by a confluence of hereditary and environmental variables, while its specific etiology is yet unknown.
Genetic factors: RA frequently runs in families, and some genetic differences increase the risk of developing the disease. Though not everyone with a family history of RA will get the condition, genetics alone cannot fully explain how RA develops.
It’s possible that specific environmental factors contribute to the emergence of RA. Toxins or infections, for instance, might cause the immune system (IS) to start attacking the joints and cause RA. Another established risk factor for RA is smoking.
It is significant to remember that RA development is complicated and poorly understood. The illness is most likely the result of a confluence of hereditary and environmental factors. It is crucial to contact with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan if you have any health concerns or are exhibiting symptoms that could indicate RA.
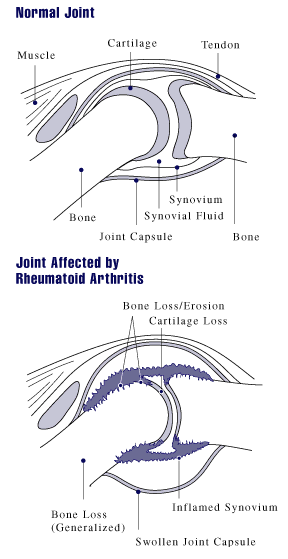
What Happens to the Joints:
The immune system of the body accidentally attacks the joints, causing swelling and thickening of the joint capsule. In the affected joints, this may result in discomfort, stiffness, and edema.
As a chronic autoimmune condition, RA causes the IS to assault the body’s healthy cells. This causes swelling and tissue damage.
The underlying bone and cartilage may also become inflamed as a result of RA. This may cause function loss and joint deformities over time. Inflammation in other body organs, including the lungs and blood arteries, can also be brought on by RA.
In order to control symptoms and enhance general health, lifestyle changes are frequently combined with drugs to reduce inflammation and avoid joint injury. It is crucial that you contact a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan if you have any health concerns or are exhibiting symptoms that could indicate RA.
Diagnosis:
A detailed medical history, physical examination, and a person’s signs and symptoms are frequently used to make the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
X-rays and laboratory tests can be used to confirm a diagnosis of RA or rule out other illnesses with similar symptoms. X-rays can reveal RA-related abnormalities in the joints, such as bone degradation and joint deformity.
RA can also be diagnosed through laboratory studies. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein blood tests, for instance, might both show higher levels in RA patients (CRP). Blood tests can also be used to assess the body’s levels of certain proteins known as antibodies, which are frequently found in RA patients.
No single test can accurately diagnose RA. On the basis of a person’s signs and symptoms, medical history, and test results, RA is frequently diagnosed. It is crucial to consult a doctor if you have any worries about your health or are displaying symptoms that could indicate RA.
Here are some Resources:
Autoimmune diseases:
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS): This organization, which is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), provides information on a wide range of musculoskeletal and skin conditions, including autoimmune diseases. You can find more information on autoimmune diseases, including causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment, at the following link: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/autoimmune-diseases
- American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA): This organization is dedicated to improving the lives of people with autoimmune diseases and their families. You can find more information on autoimmune diseases, including a list of common autoimmune diseases, at the following link: https://www.aarda.org/autoimmune-information/
- Mayo Clinic: This organization is a trusted source of health information and provides detailed information on a wide range of medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases. You can find more information on autoimmune diseases, including causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment, at the following link: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/autoimmune-diseases/symptoms-causes/syc-20353443
RA Specific Information:
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS): This organization, which is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), provides detailed information on RA, including causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. You can find more information on RA at the following link: https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/rheumatoid-arthritis
- Arthritis Foundation: This organization is dedicated to improving the lives of people with arthritis, including RA. You can find more information on RA, including tips for managing the condition, at the following link: https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/rheumatoid-arthritis
- Mayo Clinic: This organization is a trusted source of health information and provides detailed information on RA, including causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. You can find more information on RA at the following link: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20350377