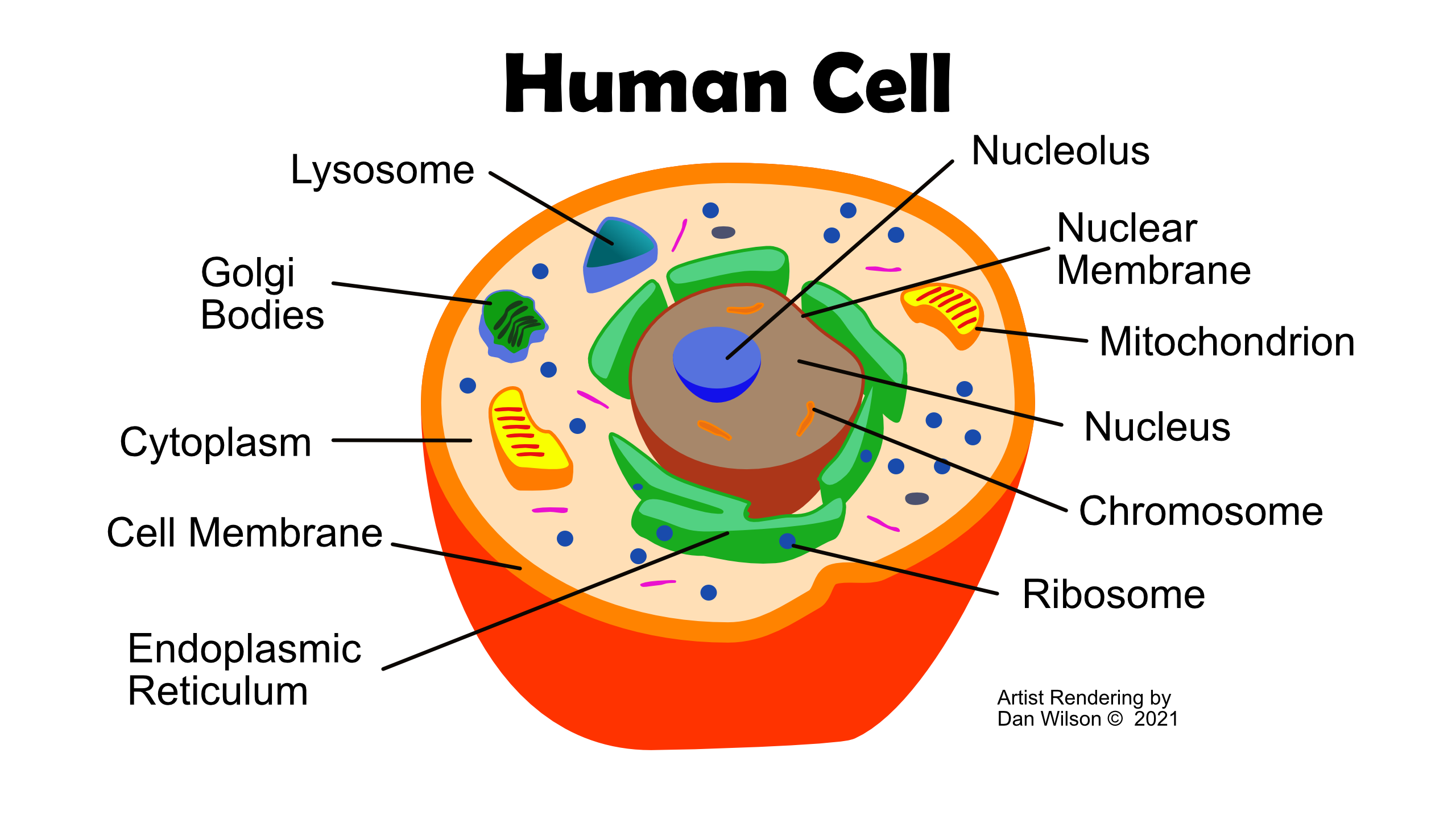
From the Latin cellula, or “small room”, cells are found in various forms throughout the body. Most types of cells have a nucleus, while red blood cells do not. Only sperm cells have a flagellum or tail.
Here is a breakdown of the cell structure:
- The Nucleolus is the prominent structure of the nucleus and produces the ribosomes
- Ribosomes are produced by the nucleolus and link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) consists of the rough ER and the smooth ER. Found in most cells, it is involved in protein folding.
- Golgi Bodies are sometimes called Golgi apparatus or complex. It packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before they are sent to their destination.
- Lysosomes break down many kinds of biomolecules. They are the waste disposal unit of cells.
- Chromosomes are long DNA molecules or parts thereof that play a significant role in transcriptional regulation. They are visible under a light microscope during the metaphase of cell division.
- Most human cells have a nucleus, while some have many and some, like red blood cells have none. The nucleus acts as the cell control center and carries most of the genetic information, except for the mitochondrial DNA.
- A mitochondrion is a double membrane organelle found in most human cells. It generates most of the adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) and is called the powerhouse of the cell.
- Nuclear Membrane or nuclear envelope encases the nucleus which contains the genetic material. It is composed of two membranes with a pronuclear separating them. The membrane is also continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane.
- Cytoplasm is the material between the nucleus and the cell membrane. It is about 80 percent water and contains the various organelles.