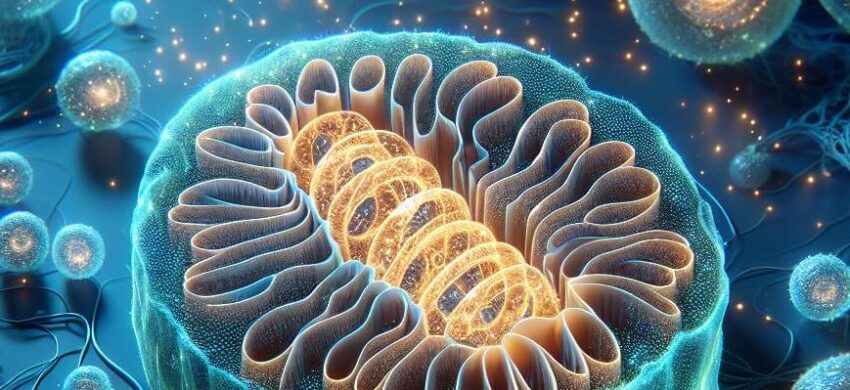
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell due to their role in producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main source of energy. They are unique among organelles as they contain their own DNA and can reproduce independently within the cell.
These double-membraned organelles influence many cellular processes beyond energy production. This includes calcium signaling, which is crucial for the functioning of several cellular activities, and cell death pathways, thereby controlling the life cycle and death of a cell.
Mitochondria play a vital role in maintaining the overall health of a cell. They help in maintaining correct ion balance and in managing the normal physiology and metabolism of a cell.
Because of their critical role, any malfunction within the mitochondria can result in severe diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and various neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Hence, understanding the role of mitochondria in cellular activity is key to advancements in healthcare.
Their floating nature within the cell and importance underscore their central role in sustaining life.
 |
 |